What Should a Motor Carrier Do When They Get a Drug & Alcohol Clearinghouse Alert?
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration is now notifying motor carriers if a driver’s Drug and Alcohol Clearinghouse record changes within 12 months after their last query.
Previously there was a loophole in the Clearinghouse system where a driver could have a drug or alcohol violation reported after a pre-employment query, but if another carrier went to hire that driver before their next annual Clearinghouse check, they wouldn't necessarily know about the prior violation.
Previously, such alerts were limited to 30 days following pre-employment queries. This change should help carriers identify violations occurring under another motor carrier’s drug or alcohol testing program.
Employers are now notified by email when a driver with a query has new information placed on his or her record. Changes in a driver’s Clearinghouse record that might prompt an alert from the FMCSA include:
- A new violation (failed test, actual knowledge, or a refusal to test);
- An entry from a substance abuse professional (SAP);
- A negative return-to-duty test; or
- A completed follow-up testing program.
When a motor carrier receives an alert that a driver’s record has changed, it should:
- Request a full query within 24 hours, and
- Verify the driver’s status (prohibited or not prohibited).
Motor carriers must pull the driver from safety-sensitive functions if an unresolved testing violation is discovered.

The vast majority of drug and alcohol violations are found via testing.
1. Request a follow-on query
Motor carriers should request a full (follow-on) query within 24 hours of Clearinghouse notifications.
A full query requires that the driver provide consent through a personal Clearinghouse account. If a driver does not have an account, one must be created quickly.
Once a query request is made, the driver must give consent. If the driver fails to create an account or refuses to consent, the driver cannot return to safety-sensitive functions until the issue is resolved.
If the full query shows an unresolved testing violation, the driver cannot return to safety-sensitive functions until the necessary return-to-duty steps are completed and submitted to the Clearinghouse.

A prohibited status means the driver has not completed the necessary steps to return to duty, including a substance abuse professional (SAP) evaluation, treatment, and a negative drug and/or alcohol test.
If the change to the record was the result of the completion of a follow-up testing program or the entry of a negative return-to-duty test (Not Prohibited status), the driver can continue perform safety-sensitive functions.
2. Change annual query rotation
Once every 365-day period, motor carriers must request an annual Clearinghouse query on drivers in positions requiring a commercial drivers license. Requesting a Clearinghouse query before the 12 months resets the rotation.
That means a follow-on Clearinghouse query:
- Satisfies the annual query requirement, and
- Allows motor carriers to change their annual rotation schedule based on the follow-on report date.
When a motor carrier receives notification that a driver’s Clearinghouse record contains new information, a follow-on query should be requested within 24 hours to confirm the driver is not prohibited from operating a commercial motor vehicle.
Join the NorthAmerican Transportation Association’s
Drug and Alcohol Program with over 23,000 collection sites all across the U.S.

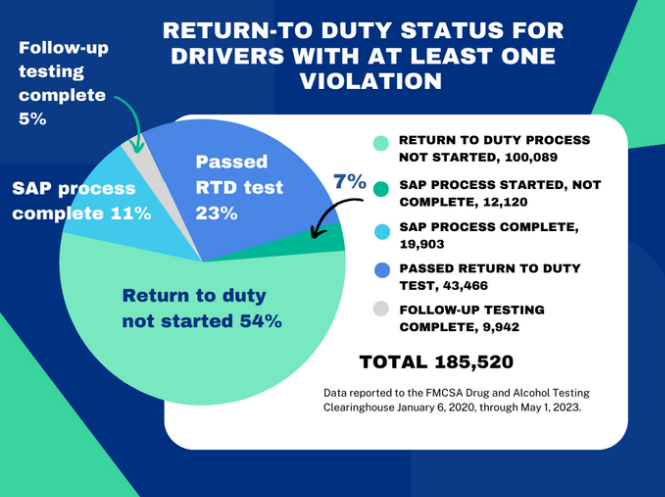
Since the launch of the CDL Drug and Alcohol Clearinghouse on January 6, 2020, through May 1, 2023, 71% of drivers with at least one reported violation remain in a “prohibited status.”
Content Disclaimer: Due to the constantly changing nature of government regulations, it is impossible to guarantee the total and absolute accuracy of the material contained herein or presented. NorthAmerican Transportation Association (NTA) cannot and does not assume any responsibility for omissions, errors, misprinting or ambiguity contained. NTA shall not be held liable in any degree for any loss, damage or injury caused by any such omission, error, misprinting or ambiguity present. It is made available with the understanding that NTA is not engaged in rendering legal, accounting or other professional service. If legal advice or other expert service is required, the services of such a professional should be sought.











